Busbars are key elements in many electrical distribution network systems, such as switchgear assemblies, electric vehicle charging infrastructure, renewable energy systems (solar/PV wind), data centers, industrial electrical panels, substations, and manufacturing sites. With increased power density and lower dimensions in each component in order to meet this demand, more reliance is placed on the reliability/performance of the busbar. Even though busbars are built to withstand extreme conditions, they can still fail. A failed busbar could result in power outages, overheating, fire hazards, electrical equipment destruction, and a large amount of lost time due to downtime (i.e., cost of service).
This guide will describe the different types of busbar failures, analyze reasons for these failures, present different means by which to diagnose, and identify some proven methods for preventing busbar failure.
A busbar is a metal strip or “bar,” commonly made from copper or aluminum, that is used in many electrical applications to carry current with minimum resistance, resulting in maximum efficiency. Busbars will replace traditional cabling for many high-current-carrying applications because they provide the following advantages:
Lower electrical losses
Improved heat dissipation
Reduced overall size
Improved current carrying capability
However, busbars may experience premature failure due to:
Design considerations
Material selection
Installation errors
Environmental exposure
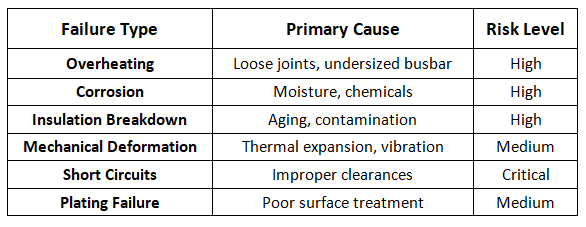
1. Busbar Overheating
What Causes Busbar Overheating?
Loose bolts or connections.
The busbar is too small (copper or aluminum).
There is high contact resistance.
Current is not distributed evenly.
Oxidation develops on contact surfaces.
How to Diagnose Overheating
Use an infrared thermography camera to locate hotspots.
Look for visible signs, such as discoloration or burnt insulation.
Measure voltage drops across joints to determine if overheating is occurring.
How to Prevent Overheating
Select properly sized busbars (with respect to their rated current).
Use the proper torque when installing.
Use tin plated copper busbars to limit the potential for oxidation.
Tighten bolted joints periodically during maintenance.
2. Corrosion and Oxidation Failure
Reasons for Corrosion
The product is located in a high-humidity environment.
The product is located in a chemically aggressive environment (e.g., near industrial plants).
The product is exposed outdoors without adequate protection.
Dissimilar metals are being used together (for example, copper to aluminum), creating galvanic corrosion.
Diagnosis of Corrosion
Presence of white or green powdery deposits on either aluminum or copper surfaces when inspection is performed.
Resistance increases during electrical testing.
Pitting or rough surface when visual inspection is performed on the joint.
Prevention of Corrosion and Oxidation Failure
Use protective coatings or sleeves.
Use sealed enclosures with an IP rating.
Avoid using copper and aluminum together without having a bimetallic connector installed.
3. Insulation Failure of Busbars
Common Causes of Insulation Failure
Aging of the insulation materials.
Overheating cycles.
Dust, oil, or moisture entering the insulation.
There is not enough clearance between conductors (creepage and clearance distances).
Identification of Insulation Failure
Partial discharge testing.
Visual evidence of cracks or peeling.
Electrical leakage or short-circuiting.
Prevention of Insulation Failure
Use sleeved aluminum busbars or epoxy-coated busbars.
Follow IEC and IS standards for spacing
Regular cleaning and insulation resistance testing
4. Mechanical Stress and Strain
Mechanical Failure Happens Due To:
Thermal expansion and constriction.
Lack of strength or secure mounting.
Vibration (generators and EV charging stations).
Short circuit forces from fault currents.
How to Identify Mechanical Failure:
Misalignment of busbars.
Cracked angles and joints.
Audible sound and vibration.
Preventative Measures Against Mechanical Failure
Use flexible connectors at expansion joints.
Provide appropriate support / bracing.
Design busbars with appropriate bend radii.
Ensure conformity with short-circuit withstand values.
5. Short Circuit and Flashover Failures
Causes of Short Circuits/Flashover
Lack of phase-to-phase clearances.
Presence of contaminants (dust or moisture) on the surface of insulation.
Insulation coordination issues.
Improper installation practices.
Methods Used to Determine Failures
Burn traces / Arcing traces.
Sudden tripping of protection devices.
Damage to adjacent components.
Methods Designed to Prevent/Reduce Failures
Proper Air & Creepage Distances
Insulated busbars or sandwich busbar systems.
Inspections should be performed dielectrically & visually on a regular basis.
6. Plating and Surface Treatment Failure
Why Plating Fails
Poor quality plating process
Insufficient thickness
Mechanical damage during installation
How to Detect It
Peel-off/flaking of tin/silver layer
Rapid oxidation after a short usage period
Prevention
Purchase from certified copper busbar manufacturer in Delhi/NCR.
Specify minimum thickness of plating
Carefully handle busbars during installation
Check joint torque values
Scan hotspots with thermal camera
Inspect insulation and plating
Measure voltage drop and resistance
Check for corrosion/moisture
Industry Standards to Be Adhered to
IEC 61439 (Low-voltage switchgear assemblies)
IEC 60865 (Short-circuit forces)
IS 8623 / IS 8084
Adherence to standards minimizes the chances of failure.
Often, the cause of failure is not operational but design and manufacturing-related. Partnering with an experienced aluminum busbar manufacturer in Delhi means:
Proper material choice
Accurate manufacturing
Consistent plating quality
Adherence to country and global standards
This is particularly important for EV charger busbar suppliers, switchgear manufacturers, and renewable energy system integrators.
Preventive maintenance is one of the best ways to prevent unexpected busbar failures and extend the life of the system.
Recommended Maintenance Schedule
Monthly visual inspection for signs of discoloration, dust, or moisture
Quarterly torque verification of bolted connections
Annual thermal imaging and insulation resistance tests
Immediate inspection following a short-circuit or overload occurrence
Environmental Controls
Maintain controlled temperature and humidity conditions
Install space heaters or dehumidifiers as needed in panels
Provide adequate ventilation for heat removal
Most failures occur during the design stage rather than during actual operation.
Common Errors when Designing for an Electrical Bus System
inappropriate assumptions of current density
short-circuit force impact ignored
Insulation spacing does not provide proper insulation coordination.
selection of copper or aluminum busbar material
How to Prevent Design Errors
follow IEC and IS standards absolutely
Perform simulation and load analysis during design
Consult busbar manufacturers with experience.
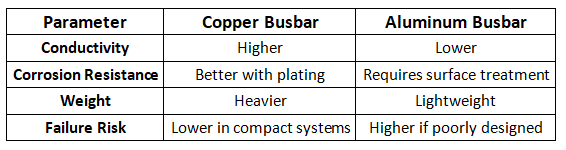
Choosing the right material significantly impacts long-term reliability.
The following are the main deployment applications where busbar failures may result in decisions with significant impacts on operations or finances even though they occur in small ways.
Electric vehicle charging stations
Solar and wind energy installations
Data center and information technology infrastructure
Industrial automation control panels
Power distribution board and substation
All of these locations will incur extensive costs when busbars fail regardless of how large the failure is or how small it is.
What is the most frequently reported type of busbar failure?
Loose connections, improper torque, undersized busbars, or high contact resistance at joints are the most common causes of busbar overheating.
How can you determine whether a busbar has failed?
Thermal imaging, resistance measurement, visual inspection for discoloration or deformation, and partial discharge testing for critical systems are all methods of verifying a busbar’s condition.
Is there a risk of a fire due to failure of a busbar?
Yes, if left uncorrected, busbar failures will produce conditions that may lead to serious fire hazards, overheating, insulation deterioration, arcing, and short circuits can all contribute to fire.
What is the earliest indication of a busbar problem?
Abnormal temperature increases detected through thermal imaging, visible corrosion or discoloration, loose joints, unusual odors, and increased contact resistance are all signs that your busbar may be developing a problem.
What is the expected lifespan of a busbar?
A correctly designed, installed, and maintained busbar typically has an expected life of 20-30 years or longer, depending upon its operating conditions and load cycles.
What is the expected lifespan of a copper busbar?
High-quality copper busbars should last 25-30 years, and possibly longer, if correctly installed, torqued, and maintained routinely.
Are copper busbars better than aluminum busbars?
Copper busbars provide superior electrical conductivity and thermal performance compared to aluminum, whereas aluminum busbars tend to cost less and are lighter than copper when sized and installed properly.
Final Thoughts
Faults in busbars are not sudden; they occur gradually as a result of thermal, mechanical, electrical, or environmental factors. Knowledge of the failure process, early warning signs, and preventive measures can significantly enhance the reliability and safety of the system.
For switchgear suppliers, EV infrastructure builders, and industrial power consumers, it is important to invest in quality fabricated busbar or aluminum busbars.
Association with a reliable busbar manufacturer can help in accurate fabrication, proper material choice, and quality, thus curtailing failures at the outset.
For any query, please call us, email us or fill the form and wewill contact you shortly.
+91-9899772424
+91-9899335858
abhinavjain2001@hotmail.com
info@adinathenterprises.com